Millions of tons of plastic waste have piled up in oceans, rivers, and landfills annually. It is a significant environmental problem with long-term ecological impacts from harming marine life to greenhouse gas emission contributions. Recycling all plastic types is a better way to address this by saving natural resources and energy and reducing pollution. Since they come from already used materials, recycled plastics can actually be processed into new products thereby reducing the need for virgin plastic entirely.
Once processed, reused plastics are incorporated into eco friendly manufacturing, and industries can perform their responsibilities according to the current trend of sustainability; they can create products from sustainable plastic materials that ensure both environmental and consumer requirements. In this way, the amount sent into landfills as well as upsetting ecosystems decreases, but more importantly, it performs in sync with global targets: meeting the circular economy-the reutilization, changing, and recycling of resources. Consider a few benefits recycled plastics have over traditional raw materials like saving raw material resources and reducing carbon footprint.
What are Recycled Plastics?
These are plastics that were previously used and processed for reuse in the production of new products. This falls under a more holistic strategy towards sustainable plastic materials where waste materials are given a second life and the reduced raw resources reliance. Recycled plastics are construed as friendly to the environment as they minimize the effects of environmental degradation associated with production, as is the case with virgin plastics manufactured directly from petrochemical sources.
The sources of recycled plastics are found to be numerous, ranging from plastic packaging of everyday life of consumers such as bottles and containers, to post industrial wastes produced at the point of manufacture. Rather than breaking it down, cleaning, and then forming it into pellets or fibers, all these materials are recycled for creating new objects instead of fresh plastics production.
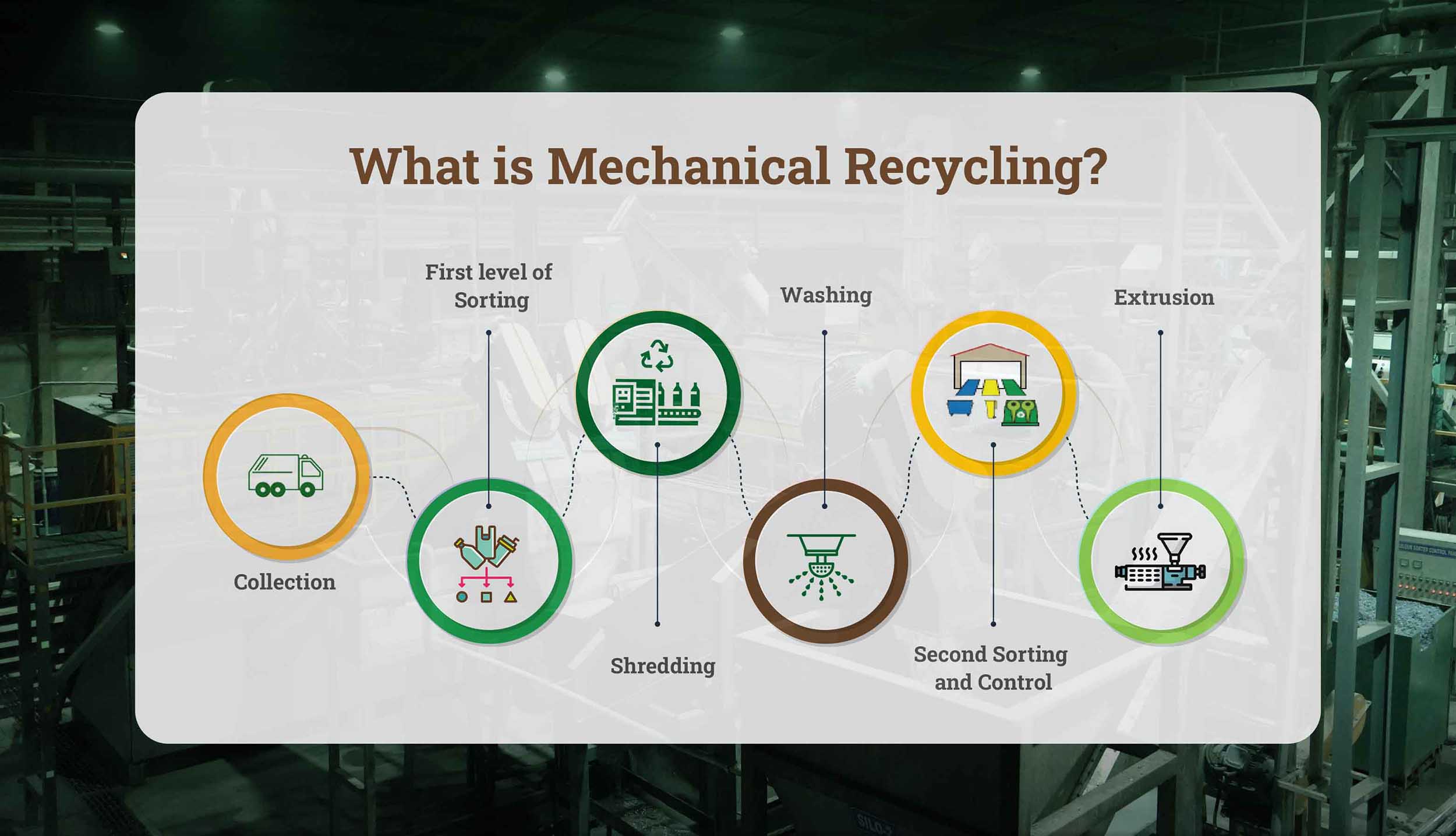
Such approaches include several that have been developed in pursuit of plastic recycling, such as the mechanical recycling and chemical recycling, which are two of the most important ones. Mechanical recycling breaks plastics down into smaller pieces through fragmentation processes that enable remolding to new product lines. Chemical recycling breaks up the plastic at the molecular level, thus enabling such broken-down materials to be changed into material of almost virgin-like quality. Such repurposing methods of plastics conservatively save resources because they avert or reduce waste in landfills.
Thus, reused plastics are advantageously used in green manufacturing to produce cheaper goods that are also relatively environmentally friendly.
The Different Types of Recycled Plastics
There are different types of plastics that can be easily recycled. Understanding the various types of recyclable plastics is essential in identifying unique applications and its benefits for ecologically-friendly manufacturing. Each group of recycled plastic possesses specific properties and is identified according to the resin codes, making it applicable for specific use. Let’s take a closer look at the most common ones:
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET):
- This plastic is one of the most recycled kinds of plastics for the reasons of its high clarity and strength. PES can be further processed into fibers for clothing, carpets, insulation, and other new containers of food and beverage. This makes it suitable as well as recyclable to look attractive for sustainable manufacture in the textile as well as the packaging industry.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
- HDPE is tough and resistant to chemicals. Such household items containing this plastic are milk jugs, shampoo bottles, and detergent containers. This plastic is most commonly recycled in piping, plastic lumber, and some playground equipment as well as back into new bottles. HDPE is dense and heavy, making the application of products qualify for structural integrity, thereby being a reliable material source for recycled products.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC):
- PVC is a tough, strong plastic often used in piping and medical supplies or occasionally building products. Although not as common due to its complex chemical makeup, PVC recycling can be applied in durable applications like flooring and window frames. The recycling of PVC is gaining momentum since improved methods are being developed. Therefore, it’s a feasible, even if limited, source for certain sectors of industry.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE):
- LDPE is flexible and has been widely used for plastic bags, films, and many containers, although its recycling is a bit more difficult and requires being recycled to be reused again for purposes like making trash can liners, floor tiles, furniture, or shipping envelopes. LDPE’s recyclability is now becoming greater than before, hence it now allows manufacturing of stronger and more functional products.
Polypropylene (PP):
- This versatile plastic is used for everything from food containers to automobile parts. Polypropylene can be recycled to produce cases for batteries, signal lights, storage bins, and even furniture designed for outdoor use. Because of its strength and resistance to heat, PP proves to be a highly valuable material for use in recycled manufacturing, especially for products that are expected to last under stress.
Each type brings distinct attributes to eco-friendly production processes and, therefore, increases the sustainability and efficiency of the production process. By knowing the benefit and limitation associated with each one, a manufacturer will thus make better decisions regarding incorporation in products and reduce waste while promoting sustainability.
How Recycled Plastics Contribute to Eco friendly Manufacturing?
Using recycled plastics is thus crucial because it reduces the necessity for virgin plastic manufacturing and backs the promotion of the sustainable model of manufacturing. The most palpable of these advantages is the resource saved. Recycling of plastics can go a long way in conserving precious raw materials, thereby decreasing the requirement to extract and refine new sources. There is also the aspect of saving energy: it requires less energy to manufacture with recycled plastics than it does to manufacture new plastic from raw materials so that the use of energy is also brought down. There is a significant emission reduction: recycling processes emit fewer greenhouse gasses, further reducing the carbon footprint that is tied to the traditional manufacturing process. Last, recycling plastic waste eliminates plastic waste being dumped in landfills. Such a measure helps maintain an environment and enhances smooth disposal practices. In general, these reasons make recycled plastics a significant aspect of the circular economy and responsible manufacturing.
Benefits of Using Recycled Plastics
Recycling plastics in production is a smart move for the planet and the pocket. It swaps out new plastics for recycled ones, saving natural stuff like oil and cutting down on fossil fuels. This fits nicely with our goals for a greener planet. Plus, it takes less energy to make something from recycled plastics than from new ones. This is more energy-saving, and it also makes our carbon footprint smaller. That’s a big thumbs-up in the fight against climate change and for tidier production habits. By recycling, we’re also tackling the huge problem of plastic waste. We’re keeping plastic out of dumps, seas, and the great outdoors. This helps us manage waste better and make our ecosystem healthier. On top of the green gains, using recycled plastics also chimes with the “circular economy.” This system is all about reusing things instead of throwing them away. With recycling, businesses can help feed this circular process. They can turn waste into something worthwhile and take some pressure off the planet.
The Future of Recycled Plastics in Eco-friendly Manufacturing
Recycled plastics hold a bright future in green production, encouraged by advancements in technology and supportive rules. New recycling methods, like chemical recycling, make recycled plastics almost as good as new ones. This opens up more ways they can be used – even in areas where the quality of material matters a lot. Also, these methods let us recycle plastics that were tough to recycle before, growing green manufacturing possibilities. At the same time, across the globe, policies and regulations are nudging businesses to go for recycled stuff. From governments to organizations, there are big goals set on plastic recycling and prizes for green habits, pushing industries to use recycled plastics. These plastics are now seen as a real and sustainable switch from new plastics. All these changes show a firm future for recycled plastics, hinting at a wide acceptance and a tie-in with care for the environment and sustainability.
Conclusion
The use of recycled plastics in green manufacturing is a good step toward sustainability. It is important to understand which types of plastics can be recycled and the benefits they offer, so that informed decisions can be made which lead to reduced environmental harm, the saving of resources, and a more circular economy. Reclaimed plastics will, therefore, prove beneficial not only for businesses but also for the greener planet.
FAQ's
What challenges exist in using recycled plastics in manufacturing?
There’s a few issues with using recycled plastics. First off, they aren’t always as good as brand-new plastics, which can mess with the way things are made. Some kinds of recycled plastics need to be sorted and treated specially, and that can be pricey and complicated. Plus, extra elements mixed into the recycled plastics could make the finished products not as good, so we need extra steps to clean it up. To deal with all this, we gotta improve our recycling methods and keep a close eye on quality to make sure the recycled plastics are strong and safe enough for use.
How are post-consumer and post-industrial recycled plastics different?
Recycled plastics can come from two places. Post-consumer plastics are from things folks used and tossed, like soda bottles or your instant noodle cup. We collect, wash, and process these to make new stuff. On the other hand, post-industrial plastics are bits and pieces left over from making things. They never made it to the folks, but we can still use them. Recycling post-consumer plastics helps clean up our environment, while post-industrial recycling reduces waste inside factories.
Are recycled plastics as durable as virgin plastics?
Most of the time, recycled plastics can be almost as good as new plastics, especially if we use top-notch recycling methods. But, sometimes recycled plastics might not be quite as strong or long lasting due to changing materials and quality drops over time. Still, they’re plenty good enough for a lot of uses, like products that don’t need to carry heavy loads or need to bend without breaking, like wrapping or everyday items.
Is recycled plastic eco friendly?
Yes, recycled plastic is generally better for our world than new plastic. When we recycle, we don’t need to make as much new plastic which saves the earth’s resources, uses less energy, and emits fewer greenhouse gasses. It also helps to keep plastic trash away from dumps and seas, making our environment healthier. By reusing instead of chucking, recycled plastics lessen the environmental impact of plastic stuff and help to keep manufacturing green.


 What is Thermoplastic? Examples & Key Benefits
What is Thermoplastic? Examples & Key Benefits What is Mechanical Recycling? Steps, Benefits & Challenges
What is Mechanical Recycling? Steps, Benefits & Challenges What is Rigid Packaging Its benefits, and Examples
What is Rigid Packaging Its benefits, and Examples What is the Impact of Plastic on the Environment?
What is the Impact of Plastic on the Environment?  Plastic Waste Management Rules in India
Plastic Waste Management Rules in India