Plastic pollution is perhaps one of the biggest environmental issues of our time. Besides causing the disruption of ecosystems and posing threats to wildlife, it also threatens human health. The core causes of plastic pollution include improper waste disposal and their immense use in individualistic applications. Every year, billions of tons of plastic waste enter our natural system and add to the worsening global problem. This has had serious impacts of plastic pollution on the environment, such as soil, water, and atmospheric contamination. Thus, the effects on the environment due to plastics are long-term, as they take thousands of years to decompose, while further decomposition creates smaller pieces of harmful microplastics that find their way into our water systems, affecting the food chain and biodiversity. Sources of plastic pollution are industrial processes of manufacturing and routine daily activities in which the consumer is a participant. Plastic pollution consequently demands change at the systems level and at the personal level and has much to be shared among nations. An integrated approach combining sustainable practices, innovative technologies, and global cooperation would therefore require countering the increasing harmful effects of plastic pollution. The state requires an all-inclusive, integrated approach, involving sustainable practices, innovative technologies, and cooperation at the global level, towards minimizing plastic pollution.
What is Plastic Pollution?
Plastic pollution refers to the physical accumulation of plastic material within the environment, damaging the ecosystems, wildlife, ocean, and health of human beings. In reality, billions of tons are produced annually, and the majority find their way into habitats where it was not intended to stay. The problem arises due to the fact that plastic is not biodegradable but remains in the environment for hundreds of years. From the top of mountains to the bottom of oceans, even the earth’s most accessible space has plastic waste traces.
To that end, improper dumping methods, the constant emergent trends of over-reliance on single-use plastics, and poor recycling systems all fuel the problem. These keep feeding a self-feeding cycle, in which wasted plastic contaminates soil and air as well as water. This includes marine life as one of the worst-affected sectors, with animals mistaking plastic for food to eat or getting entangled. In the effects of plastic pollution, there is environmental damage but also human health risks in the form of toxic chemicals and microplastics that infiltrate food chains.
Proper consumption, efficient waste management, and the latest innovative plastic waste solutions are aimed at fighting plastic pollution. All together will dampen the ever-growing impact of plastic pollution, thus paving the way for a healthier planet.
What are the major Causes of Plastic Pollution?
Major causes of pollution are by various human activities and systemic issues, leading to significant environmental damage. To stop plastic pollution, it is essential to address these root causes and implement sustainable solutions. Over 460 million metric tons of plastic are produced every year for use in a wide variety of applications.
An estimated 20 million metric tons of plastic litter end up in the environment every year. That amount is expected to increase significantly by 2040 and is a major plastic pollution cause. To stop plastic pollution, it is essential to address these root causes and implement sustainable solutions.
Overuse of Single-Use Plastics
Among the leading contributing causes of the overuse of disposable products, including bags, bottles, straws, and packaging materials, is the failure to recycle them, which eventually find their way into landfills, water bodies, and the natural environment.
Inefficient Waste Management
The collection, segregation, and recycling of plastic waste do not have an adequate system in most regions; therefore, plastics are mainly burnt, buried, and exposed to the open environment, causing great pollution around.
Inappropriate Disposal Methods
Littering and indiscriminate dumping of plastic waste in improper places, including oceans and rivers, have become very common. Directly, these practices feed into the ever-growing problem of plastic pollution.
Industrial Discharges
The plastics or plastic product-based industries generally release waste in the environment. With very little restrictions, such discharges have major impacts on pollution.
Plastics in Agriculture
Using plastics like mulch films and packages in farming brings plastic residues into the soils, negatively affecting soil health if not disposed of properly.
Lack of Awareness
This simply means that there is widespread misuse and disposal of plastics as people are unaware of the actual value of reducing plastic usage and coming out with sustainable habits.
Untrammeled Urbanization and Consumption
The rapid growth of urban areas and the increasing demand for plastic products among the consumers have really led to increased production and disposal of plastics, thereby overwhelming the municipal waste management systems.
What are the effects of plastic pollution on the environment?
Plastic pollution has a great impact on the environment, thereby leading to damage of ecosystems, animals, and human health. Animals such as turtles and seabirds ingest or get entangled in marine plastics; this disrupts biodiversity and food chains. On land, degrading plastics release toxic chemicals that contaminate the soil and groundwater, lowering fertility and killing plant and microbial life. Burning of plastic waste leads to the pollution of air and results in the release of dangerous chemicals, which accelerates climate change and health hazards as well. The effect of plastic on the environment is particularly alarming, as microplastics emerge from broken plastics that have invaded soil, water, and air, leading to long-term contamination. Land wildlife is not exempted either; animals eat plastics accidentally, and they die or suffer injuries due to this. Last but not least, the effects of plastic on the environment include a high emission of greenhouse gases due to the production and degradation of plastics. Proper sustainable practices, reduction of single-use plastics, and embracing emerging solutions to plastic waste can adequately address the causes of plastic pollution in the environment.
What are the Solutions to the Plastic Waste Problem?
Creative, sustainable efforts to eradicate plastic pollution and its catastrophic impacts have to be made at the problem-end level. Encouraging the 3Rs and reducing waste generation volume is one of the most practical measures: reduce, reuse, and recycle. A shift to biodegradable alternatives and reliance on fewer single-use plastics can greatly reduce the impacts of plastic pollution on the ecosystem. The effect of plastic on the environment can be mitigated through source segregation and investments in advanced recycling technologies, transforming sources of plastic pollution into resources with enhanced waste management systems. This approach helps reduce plastic pollution significantly by ensuring proper disposal and recycling practices.
This is achieved through coordination between governments and industries in terms of implementations of policies, such as extended producer responsibility (EPR), circular economy models, and people’s campaigns to set guidelines for appropriate consumption and community-led clean-up initiatives. By executing these plastic waste solutions, society can reduce plastic pollution and, as a result, stop further environmental degradation caused by plastic.
Conclusion
One of the global needs that requires collective urgent action is plastic pollution. Each step toward a sustainable solution is crucial, from understanding why there is plastic pollution to dealing with the impacts of plastics on the environment. Responsible consumerism, eco-friendly methods, and innovative techniques in managing plastic waste can all make a tremendous difference in lessening plastic pollution and its destructive impacts. To build a clean, healthy planet, it is much more important to find ways to stop plastic pollution than to combat the impacts by merely altering our connection with plastic. Together, we can work towards making significant progress in reducing plastic pollution and building a sustainable, bright future for the generations to come.
FAQ's
How to reduce plastic use at home?
It sometimes just takes doing small things for less plastic use at home. For instance, single-use plastic items, such as straws, bags, and bottles, could be replaced by using glass, metal, or cloth. Biodegradable or eco-friendly products must be chosen and bought in bulk. Waste segregation, where plastics are recycled, should also be prioritized. Buy products with minimal recyclable, or plastic that can be reformed and refill packaging. Advocate community-led initiatives like clean-ups or recycling drives.
Why is it difficult to reduce plastic waste?
The complexity of diminishing plastic waste arises since plastic is utilized highly, is cheaper, and is versatile, and is, therefore, an integral part of most industries as well as everyday life. The inability to access effective waste management and recycling systems only worsens the problem, while a lack of knowledge in sustainable alternatives slows change. Single-use plastics have become deeply ingrained in the consumer’s psyche; furthermore, many regions face infrastructural and economic barriers in switching over to greener solutions.
Does plastic cause global warming?
Yes, plastic contributes to global warming in many ways. Production and burning of plastics emit carbon dioxide and methane gas, as they create global warming considerably. The decomposition of plastic waste in landfills produces harmful gas, while microplastic contaminates the natural habitats, further disrupting the course of natural carbon cycles. All these climate impacts can be mitigated by making a transitional shift towards sustainable alternatives and diminishing plastic waste.


 What is Thermoplastic? Examples & Key Benefits
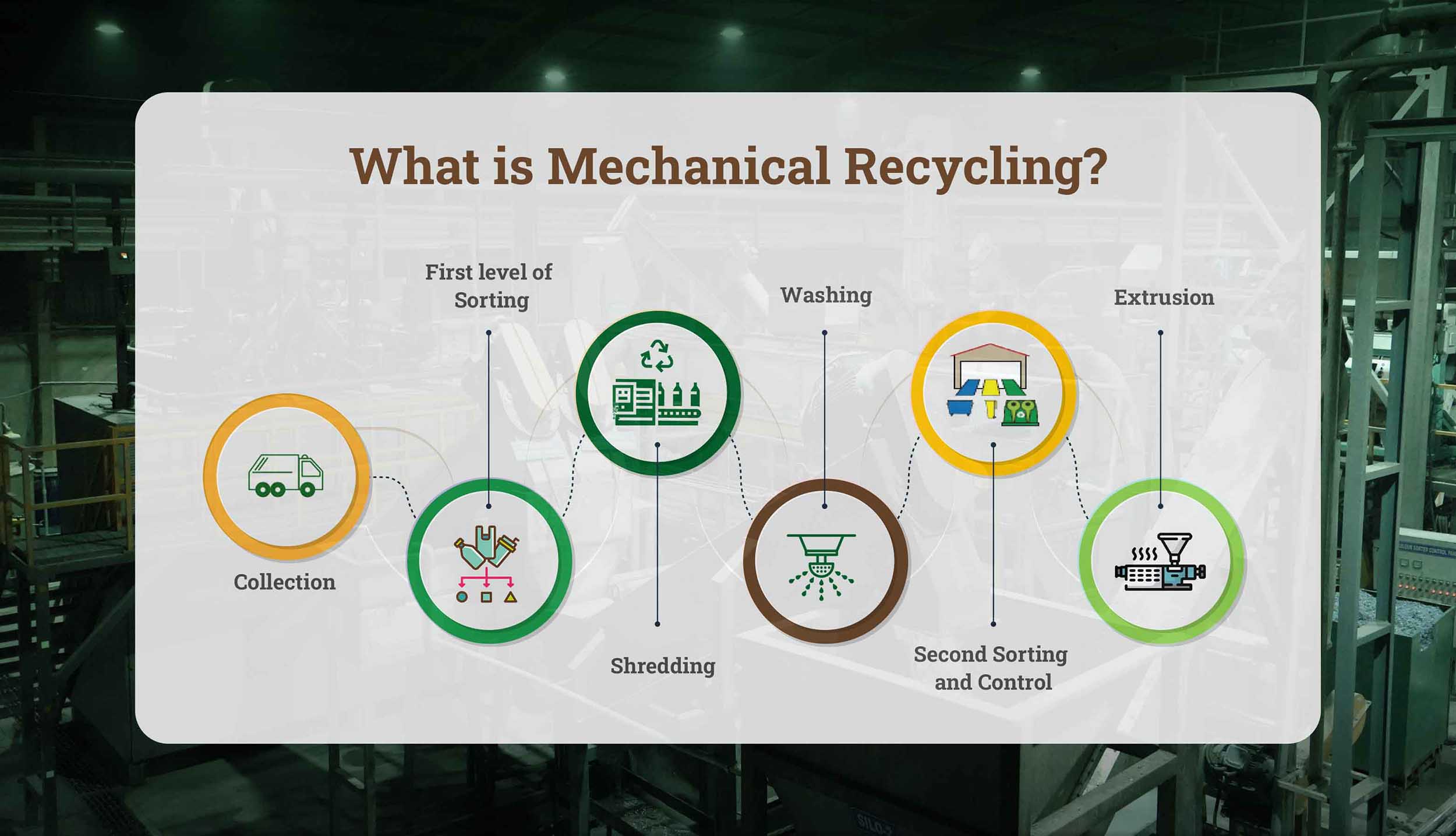
What is Thermoplastic? Examples & Key Benefits What is Mechanical Recycling? Steps, Benefits & Challenges
What is Mechanical Recycling? Steps, Benefits & Challenges What is Rigid Packaging Its benefits, and Examples
What is Rigid Packaging Its benefits, and Examples What is the Impact of Plastic on the Environment?
What is the Impact of Plastic on the Environment?  Plastic Waste Management Rules in India
Plastic Waste Management Rules in India