Mechanical recycling is the processing of plastic waste into secondary raw materials or products without significantly changing the material’s chemical structure. In principle, all types of thermoplastics can undergo mechanical recycling with little or no impact on quality. End-of-life materials can be processed via collecting, sorting, shredding, melting, and transforming them into secondary raw materials for a new application. Mechanical recycling plays a crucial role in creating a circular economy by extending the lifespan of plastic materials and reducing the need for virgin plastic production.
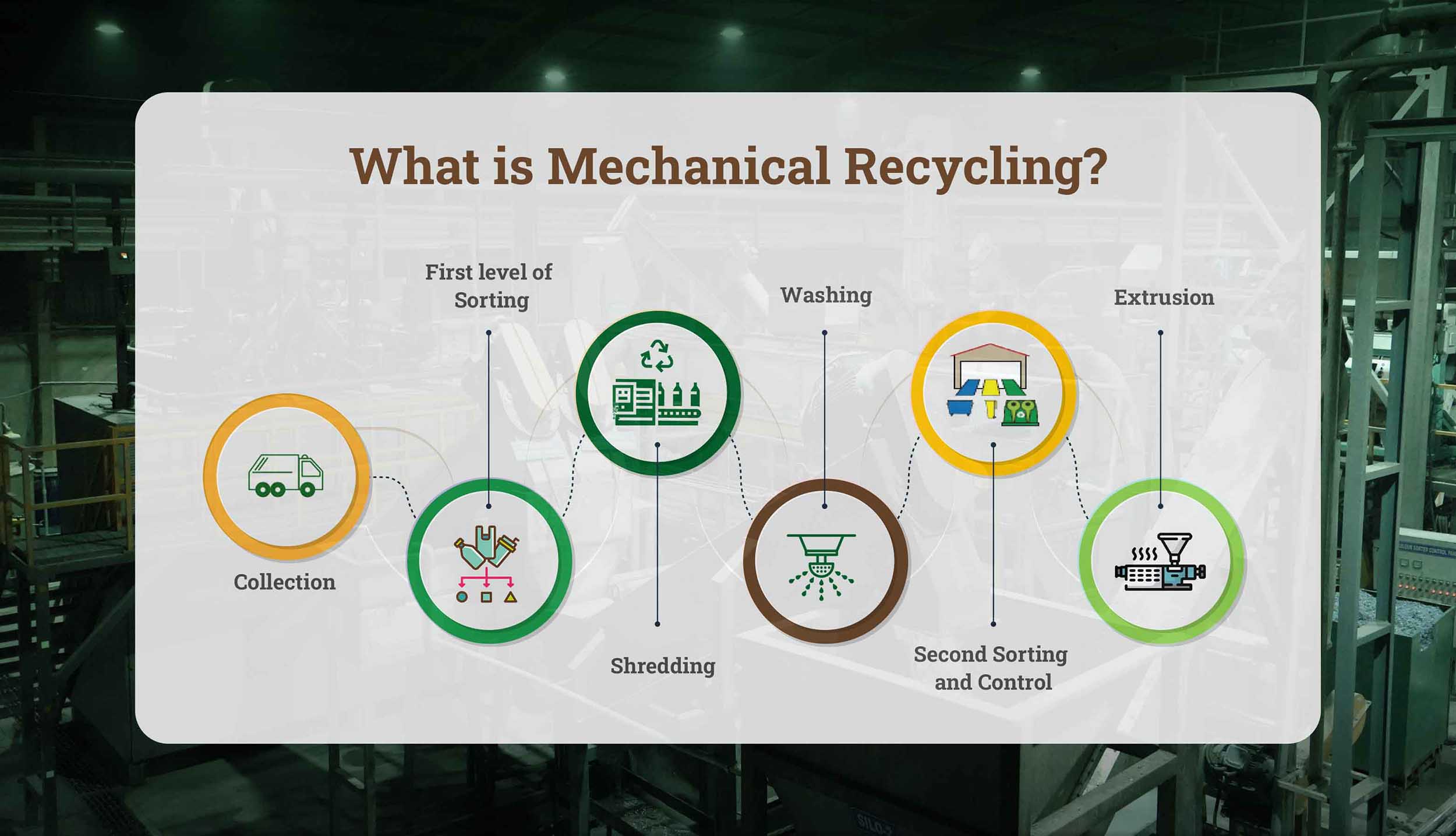
What are the steps of mechanical recycling?
Collection
Plastic waste is first gathered and separated to ensure that non-plastic materials are removed. This process is a crucial step in waste segregation, allowing for efficient recycling and reducing environmental impact.This is the initial step in the mechanical recycling of plastic, ensuring that only suitable materials enter the process.
First level of sorting
The first level of sorting occurs in the collection step, but if further sorting by thickness and color is needed, it can be done. Proper sorting enhances the efficiency of the mechanical recycling of plastic by improving material quality.
Shredding
In this stage, plastic will get shredded, further helping the process of recycling.
Washing
Washing eliminates almost 90% of the contaminations such as food, ink, glue, and all, ensuring cleaner material for the next stages of mechanical recycling of plastic.
Second sorting and control
Plastics are sorted again and controlled before being sent to extrusion.
Extrusion
Plastic flakes are finally converted into homogenous pellets ready to use in the manufacturing of new products.
Is mechanical recycling cost-effective?
- Mechanical plastic recycling can be cost-effective, but some limitations are there.
- Multi-layered plastic is complicated and not so cost-effective when compared to other plastic which have only plastic as layers.
- Market demand also affects the cost, because the more demand for recycled plastic, the more cost-effective it will be. This plays a crucial role in plastic mechanical recycling.
- Sorting and cleaning of plastic require labor costs and that will be a little expensive.
- The most challenging thing is that some plastic degrades with each recycling use, impacting the efficiency of plastic mechanical recycling over time.
What are the advantages of mechanical recycling?
The advantages of mechanical recycling are as follows:
Less waste
Accumulation of plastic waste that ends up in the landfills is significantly reduced, promoting sustainability and a circular economy.
Low energy consumption
The mechanical recycling process creates a lesser demand for plastic to be produced , resulting in significant energy savings. The production of virgin plastic requires a higher energy input.
Reduction in plastic pollution
As most plastics are recycled through mechanical recycling, a smaller amount escapes into the environment, significantly reducing plastic pollution and its harmful impact on ecosystems. Since most plastics are recycled through mechanical recycling, only a minimal amount is discarded as waste in landfills or the environment, significantly helping to curb plastic pollution.
Circular economy
Mechanical recycling of plastic promotes a circular economy as it is sustainable and beneficial for the environment.
What are the challenges associated with mechanical recycling?
Mechanical recycling of plastic has been shown to provide numerous benefits but faces a number of challenges. Sorting and cleaning them up is extremely complicated and costly. In addition, certain plastics break down in quality after they are recycled several times, becoming increasingly weak, brittle, and unfit for use. Plastics are also notoriously difficult to recycle due to their differing melting point; multi-layered plastics are particularly troublesome.
Another big hurdle is cost — virgin plastic is often less expensive to produce than recycled plastic, which makes it a less desirable option for manufacturers. Waste management is poor, so there is no segregation, due to which recycling is challenging. The main reason for this is unawareness regarding plastic pollution and its socioeconomic impact.
The quality of the recycled plastics and downcycling also becomes a problem. Recycled plastics are often facsimiles that do not retain the properties needed for the same application, preventing reuse and undermining environmental benefits.
What is the impact of mechanical recycling on the circular economy?
Mechanical recycling has a crucial role in promoting recycled plastic and reducing the need for using virgin plastic in the manufacturing process. Mechanical recycling can help extend the life cycle of every plastic and create a circular economy. For a circular economy, we have to save our natural resources and that is also happening simultaneously if we are not using our resources for virgin plastic. Furthermore, by reducing the dependence on finite raw materials, there is a support created of a more resilient and resource-efficient economy.
Conclusion
The main goal of the plastic mechanical recycling process is to reuse plastic to avoid plastic waste, save energy, and contribute to the sustainability of a circular economy. Recycling plastic waste into secondary raw materials reduces virgin plastic production, and consequently has a positive impact on plastic pollution. There are some challenges for the plastic mechanical recycling, however simple steps make a lot of difference and they will help us to take care of our planet. So let us take simple steps to make sure that we are promoting mechanical recycling which supports a circular economy.
FAQ's
What materials can be recycled using mechanical recycling?
The mechanical recycling process is for thermoplastics. This means the plastic can be melted, reshared, and used several times. This recycling mechanical method includes plastics such as:
PET
PPL
DPE
PS
Can mechanical recycling be used for all types of plastic?
No, the plastic recycling process is not suitable for every kind of plastic. Mechanical recycling definition is the process of recycling plastic waste through grinding, melting, and reworking plastic waste, converting it into a product with the same chemical composition it originally had. But epoxy, polyurethane, and bakelite are “thermosetting” polymers, making them non-recyclable because they cannot be melted down with heat.
Can mechanical recycling be done at home?
The mechanical recycling process of plastic can only be done in industries due to the complexity and high-risk factors involved, such as heat and specialized equipment.

 Understanding Single use Plastic: Impact, Pollution, and Solutions
Understanding Single use Plastic: Impact, Pollution, and Solutions What Is Solid Waste and What Are Its Effects on the Environment?
What Is Solid Waste and What Are Its Effects on the Environment? Dry waste and wet waste management – waste segregation
Dry waste and wet waste management – waste segregation Recycling and Upcycling: What’s the Difference?
Recycling and Upcycling: What’s the Difference? What Are Plastic Granules? Meaning, Types, and Uses
What Are Plastic Granules? Meaning, Types, and Uses


